Management of Neuropathy and Related Ulcers
What is diabetic neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy is the result of nerve damage from diabetes. Over half of people with diabetes have neuropathy and diabetes is the number one cause for neuropathy. However, there are other causes for such as:
- Some medications
- Advanced age
- Alcoholism
- Diseases of the nervous system
- Injuries
In diabetes, excess blood glucose can damage small blood vessels. These small blood vessels nourish the nerves. When blood vessels are damaged the nerves become damaged. These damaged nerves may cause muscle weakness and loss of sensation. Damaged blood vessels can cause tingling, pain, numbness, or weakness. The damage is often found in hands and feet first.
People with neuropathy are at high risk for development of wounds. These wounds often develop on the feet. Wounds can be caused by excessive pressure or trauma to the foot.
How is neuropathy diagnosed?
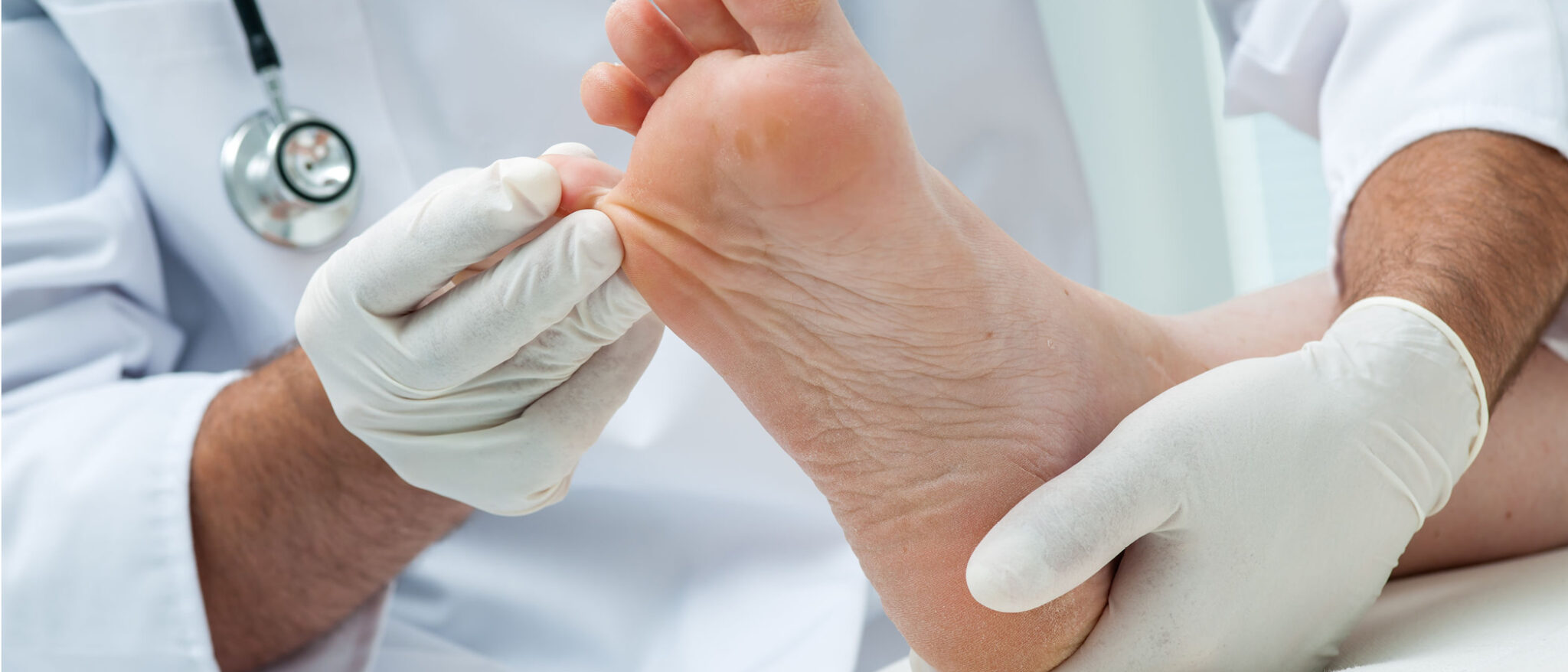
Neuropathy can be diagnosed easily and painlessly. A test is performed by a nurse at the Wound Care Center®. A thin plastic wire touches the skin on the foot. Whether or not the wire is felt can tell us if nerves have been damaged.
What does it mean if you have neuropathy?
If you lose sensation you have lost a protective feeling. You may be unaware of a rock in your shoe or rubbing a blister. These injuries can quickly lead to foot wounds. Foot wounds can be hard to heal and can end with amputation if not managed quickly.
Is there a cure for neuropathy?
There is no treatment that will heal the damaged nerves. The goal is to manage symptoms and prevent further damage.
How can I prevent or delay nerve damage on discharge?
- Inspect your feet daily for redness or sores.
- Wear special footwear.
- Protect your feet and never go barefoot.
- See a professional for nail and foot care.
- Report symptoms or worsening symptoms to your physician.
- Keep your blood sugars in the range your doctor has ordered.
- Monitor your blood sugars as directed by your doctor.
- Get a A1C at least twice a year.
- Plan meals.
- Take your medications as directed by your doctor.
- Exercise as directed by your physician.
- Stop smoking or decrease smoking as much as possible.