How to Heal Wounds Faster: Tips and Strategies for Quicker Recovery

Wondering how to heal wounds faster? There are several steps you can take. Research proves that wounds heal faster when patients stay involved in their care and follow their doctor’s advice. The most important way to help your wound heal is by keeping every scheduled appointment. However, you also need to follow good wound care practices at home. By taking an active role in your wound care and following these tips, you can promote faster healing and reduce the risk of complications.
Understand the Science Behind Wound Healing
Wound healing follows a complex sequence of four distinct yet overlapping phases:
- During hemostasis (0-several hours), platelets form clots to stop bleeding
- The inflammatory phase (1-5 days) brings white blood cells to fight infection and clean the wound
- In the proliferation phase (3-21 days), specialized cells called fibroblasts produce collagen, forming new tissue and blood vessels. This allows oxygen and nutrients to reach the wound bed, supporting the growth of healthy granulation tissue. Growth factors signal cells to multiply and migrate to the wound
- The final remodeling phase (21 days to 2 years) involves collagen reorganization and scar tissue maturation. The healed tissue gradually regains strength, though it typically reaches only about 80% of the original tissue’s strength
Factors affecting healing speed include:
- Blood supply and oxygenation
- Nutritional status
- Immune system health and function
- Age and underlying health conditions
- Local wound factors like infection or pressure
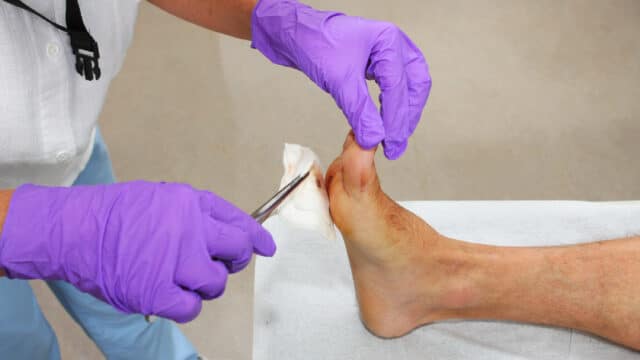
Essential First Aid Steps for Proper Wound Care
Proper wound care begins immediately after injury with thorough hand washing and stopping any active bleeding through direct pressure. Clean the wound with gentle soap and water or sterile saline solution, removing any visible debris. Apply an antiseptic and avoid hydrogen peroxide, which can damage healthy tissue.
Different wounds require specific approaches:
- Minor cuts/scrapes: Clean, apply antibiotic ointment, and cover with a sterile dressing
- Deeper cuts: Apply pressure and seek medical care if the bleeding continues or the wound is deep or gaping
- Burns: Cool with room temperature water; don’t break blisters, cover loosely, and seek medical care if the burn is deep, widespread, or in a sensitive area of the body. Err on the side of caution and seek a medical evaluation with any concerns
- Puncture wounds: Stop the bleeding, clean and cover the wound, and watch for signs of infection. Puncture wounds often require medical evaluation due to infection risk
Medical Treatments and Professional Interventions
Advanced wound care combines specialized dressings with targeted therapies based on wound type and healing stage. Moisture-retentive dressings like hydrocolloids and foams protect the wound while managing drainage, and antimicrobial dressings containing silver or iodine help control infection.
Advanced therapies include:
- Bioengineered skin substitutes for diabetic ulcers and venous wounds
- Negative pressure therapy to remove excess fluid and promote granulation
- Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for selected wounds with poor oxygen supply
- Growth factors and specialized proteins to stimulate healing
Treatment selection depends on wound characteristics, underlying conditions, and healing progress. Most chronic wounds show measurable improvement with appropriate therapy. Regular assessment ensures treatment effectiveness and allows for adjustments as needed.
Tips for Taking Care of Wounds Between Appointments
- Nutrition is an important part of wound healing – eat a well-balanced diet, following any dietary or fluid restrictions your doctor has recommended
- Stop smoking – get help with 5 Steps to Quit Smoking from the American Heart Association
- Keep pressure off your wound
- If you have diabetes, monitor your blood sugars because wound healing stops when blood sugars are over 200
- If the provider instructed you to change your dressing in between visits, examine your wound with each dressing change – be sure to wash your hands before and after each dressing change
- Keep your dressing clean and dry
- Notify your healthcare provider immediately if you notice a problem or have a concern with your dressing
Nutrition’s Role in Wound Healing
Proper nutrition provides essential building blocks for tissue repair. Protein forms the foundation, requiring 1.2-1.5 grams per kilogram of body weight daily. Vitamin C supports collagen formation, while zinc and amino acids aid cellular repair.
Key dietary recommendations:
- Lean proteins: fish, poultry, eggs, legumes
- Vitamin C-rich foods: citrus fruits, bell peppers, leafy greens
- Zinc sources: meat, shellfish, nuts, seeds
- Adequate hydration: 8-10 cups of fluid daily
Consider nutritional supplements only under medical supervision, as they may interact with medications or underlying conditions. A registered dietitian can help develop a personalized meal plan that supports optimal wound healing.
Lifestyle Factors That Impact Wound Healing
Sleep and stress management significantly influence healing rates. Quality sleep boosts immune function and tissue repair, while chronic stress impairs these processes. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep and practice stress reduction techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
Regular exercise promotes robust circulation, strengthens the vascular system, and increases oxygen delivery to tissues. When active, the body develops healthier blood vessels and improves blood flow to all areas. This enhanced circulation means that if a wound occurs, the area already has a strong foundation of blood vessels to support healing.
Key benefits:
- Improved peripheral blood flow
- Enhanced oxygen delivery capacity
- Stronger capillary networks
- Better nutrient distribution
- Reduced risk of peripheral vascular disease
These vascular improvements create a more resilient system that is better equipped to handle wound healing if injury occurs. Once an injury occurs, exercise may require modification during the healing process.
Smoking severely impairs healing by reducing oxygen delivery and constricting blood vessels. Quitting smoking, even temporarily, can significantly improve healing outcomes. Talk to your healthcare provider about smoking cessation support.
Special Considerations for Different Types of Wounds
Wound healing approaches vary significantly based on the wound’s underlying causes and characteristics. Understanding the specific requirements and challenges of each wound type allows for targeted interventions that optimize healing outcomes. While the following guidelines represent typical approaches, your healthcare provider may recommend different treatment strategies based on your specific situation and needs.
Surgical Wounds:
- Keep the incision clean and dry
- Follow post-operative instructions precisely
- Normal healing: 2-4 weeks for closure
- Monitor for signs of dehiscence or infection
Diabetic Ulcers:
- Strict glucose control essential
- Offloading pressure mandatory
- Regular debridement is often needed
- Typical healing: 12-16 weeks with proper care
Pressure Injuries:
- Complete pressure relief crucial
- Frequent repositioning
- Support surfaces as needed
- Healing varies: 2-6 months, depending on the stage
Traumatic Wounds:
- Initial thorough cleaning vital
- May require staged closure
- Watch for compartment syndrome
- Timeline varies with injury severity
Each type requires professional assessment and individualized treatment planning.
Signs Your Wound Needs Immediate Medical Care
It is essential to closely monitor your wound and call your doctor right away if you experience:
- Increased pain at the wound site
- Excess drainage that wets the dressing before the time to change
- Redness and swelling around or spreading away from the wound
- Foul odor coming from the wound
- Changes in the color of the wound or drainage
- Nausea or vomiting
- Chills or fever
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring proper wound management.
Taking Action: Your Next Steps for Optimal Healing
Healogics provides world-class wound care to help wounds heal faster at more than 600 Wound Care Centers® nationwide. Over the past 20 years, we have helped to heal more than four million wounds. We have partnerships with academic and research-based scientists to consult and analyze, driving collaboration to provide better outcomes for our patients. Our team of wound care experts uses the latest evidence-based treatments and technologies to accelerate wound healing and improve patient outcomes.
At Healogics, we understand that every wound is unique. We work closely with patients and their healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans that address the specific needs of everyone. Our comprehensive approach to wound care includes advanced therapies, such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which can help accelerate the healing process. If you or a loved one is living with a non-healing wound, don’t wait to seek specialized care. Contact a Healogics Wound Care Center® near you to learn more about our advanced treatment options and how we can help you heal faster and get back to living your best life.