Management of Venous Insufficiency

Understanding Venous Insufficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
As the nation’s leading network of Wound Care Centers®, Healogics understands the significant impact that venous insufficiency can have on your daily life and overall well-being. As experts in wound care, we see firsthand how this common condition can profoundly affect individuals. According to research by the Society for Vascular Surgery, about 40% of people in the United States have chronic venous insufficiency, with women being more likely to develop this condition than men.
Venous insufficiency occurs when the veins in your legs struggle to pump blood back to your heart effectively. In its early stages, you might notice symptoms like swelling in your legs and ankles, a feeling of heaviness or tiredness in your legs, or the appearance of varicose veins. If left untreated, these symptoms can progress to more serious issues like skin changes and venous ulcers. As the leaders in wound care, we’re committed to helping you understand this condition, recognizing its early signs, and providing tools to explore the most effective treatment options available.
Whether you’re experiencing the early signs of venous insufficiency or dealing with more advanced symptoms like venous ulcers, our team of wound care experts is here to guide you through every step of your healing journey. We focus on providing comprehensive care, from early intervention to managing complex cases, always with your comfort and health as our top priority.
In the following sections, we’ll share our expertise on the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for venous insufficiency.
What is Venous Insufficiency?
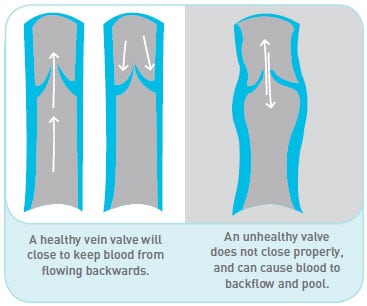
Venous insufficiency occurs when the veins in your legs don’t work properly. This means that fluid can build up in your lower legs, causing them to swell. As this swelling progresses, it can stretch your skin, much like an oversized balloon. In some cases, the stretched skin may break open, leading to the formation of a wound. You might also notice changes in your skin color, typically darkening, and your skin may feel different to the touch. These changes are all signs that your veins are struggling to return blood to your heart effectively.
Recognizing Symptoms of Venous Insufficiency
Because venous insufficiency is a progressive condition, it can develop gradually over time. Research shows that recognizing its symptoms early can lead to more effective treatment and a better prognosis, including prevention of complications. Here are the common signs and symptoms to watch for:
Early-Stage Symptoms:
- Swelling in the ankles and feet, especially after standing for long periods
- A feeling of heaviness or tiredness in the legs
- Mild aching or pain in the legs
- Itchy skin on the legs
- Appearance of spider veins or small varicose veins
As the condition progresses, you may notice:
- Increased swelling that may extend up the leg
- More pronounced varicose veins
- Dull aching, cramping, or feeling of heaviness in the legs that worsens when standing
- Discoloration of the skin, often a brownish or reddish hue
- Dry, scaly, or hardened skin on the legs
- Wounds or ulcers on the legs that are slow to heal
Advanced Stage Symptoms:
- Persistent leg swelling that doesn’t improve with elevation
- Leg pain that interferes with daily activities
- Open sores or ulcers, typically near the ankle
- Thickened, leathery appearance of the skin on the legs
- Recurring skin infections
It’s important to understand that symptoms can vary from person to person, and not everyone will experience all of these signs. However, if you notice any of these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time, please consult with a healthcare professional. Early intervention can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent the condition from progressing to more severe stages.
Diagnosing Venous Insufficiency
Diagnosis of venous insufficiency involves several key steps. Initially, healthcare providers will take your medical history, inquiring about symptoms, past health issues, and lifestyle factors that may contribute to venous problems. This is followed by a thorough physical examination, where doctors assess the legs for visible signs such as swelling, skin discoloration, varicose veins, and any ulcers or wounds.
The cornerstone of a venous insufficiency diagnosis is typically the vascular ultrasound, a non-invasive imaging test that uses sound waves to visualize blood flow in the veins. This test allows healthcare professionals to detect blockages and abnormal flow patterns and assess the overall structure and function of the veins. In some cases, additional imaging tests may be necessary. These can include venography, which uses X-rays and contrast dye to show blood flow, or CT and MRI scans for more detailed images of the veins and surrounding tissues. While not diagnostic for venous insufficiency itself, blood tests might also be ordered to rule out other conditions or evaluate overall health.
Early diagnosis is important. It allows for timely intervention, which can slow or prevent the progression of the disease and the development of serious complications like venous ulcers. Addressing symptoms early can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life and daily functioning. Also, early-stage venous insufficiency often responds well to conservative treatments, potentially avoiding the need for more invasive procedures while improving vein health.
Understanding Venous Insufficiency and its Progression to Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Venous disorders encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the veins, particularly in the lower limbs. Among these, venous insufficiency stands out as a common and potentially serious issue. At its core, venous insufficiency occurs when the veins struggle to efficiently return blood to the heart, often due to weakened or damaged valves within the veins.
If venous insufficiency persists or worsens over time, it may develop into chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), a more advanced and persistent form of the condition. The progression from venous insufficiency to CVI is not inevitable, but it underscores the importance of early recognition and management. Chronic venous insufficiency is typically diagnosed when symptoms have been present for at least three months and are accompanied by specific changes in the legs, such as edema, skin alterations, or venous ulcers. Understanding the relationship between these conditions – and how they fit within the broader spectrum of venous disorders – is essential for patients interested in managing their vein health and improving their long-term prognosis.
Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Prognosis and Management
The long-term prognosis for individuals with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the severity of the condition, how early it’s diagnosed, and how diligently it’s managed. Research has proven that while CVI is a chronic condition that typically doesn’t resolve on its own, with proper care and management, many people can significantly improve their symptoms and quality of life.
For those diagnosed with CVI, the prognosis is generally more favorable when the condition is caught and treated early. Early intervention can slow the progression of the disease, reduce the risk of complications like venous ulcers, and help maintain better overall vein health. However, even in more advanced stages, appropriate management can lead to substantial improvements in symptoms and daily functioning.
Ongoing management is vital to effective CVI care. This typically involves a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle modifications. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers allow for monitoring the condition’s progression and adjusting treatment plans as needed. These check-ups may include physical examinations and, occasionally, imaging tests to assess vein function and structure.
By adhering to a comprehensive management plan, many individuals with CVI can maintain a good quality of life and reduce the risk of complications. It’s important to remember that while Chronic Venous Insufficiency is chronic, it’s not static – active management can lead to improvements over time. With ongoing care and lifestyle adjustments, people with CVI can often continue to lead active, fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition.
Venous Ulcers: Causes and Treatment
Venous leg ulcers are open sores that typically develop on the skin between the ankle and the calf. These ulcers are a common complication of long-term venous disease, in which the veins in the legs have difficulty returning blood to the heart. Due to this underlying circulatory issue, venous leg ulcers can be stubborn and slow to heal.
People with these ulcers face an increased risk of infection, which can further complicate the healing process. Additionally, these wounds can significantly limit mobility, affecting daily activities and quality of life. While some venous leg ulcers may start spontaneously, others can be triggered by minor injuries, such as bumping the leg. In individuals with compromised vein function, even minor wounds may struggle to heal properly, potentially developing into persistent ulcers.
Causes of Damaged Veins
Various factors can contribute to vein damage, ranging from physical injuries to chronic health conditions. Understanding these causes can help in the prevention and management of venous disorders:
Physical Trauma and Medical Conditions:
- Direct injury to veins from accidents or trauma
- Blood clots (deep vein thrombosis)
- Complications from fractures or broken bones
- Previous vein surgeries or treatments
Lifestyle Factors:
- Obesity or having excessive body weight, which increases pressure on leg veins
- Prolonged periods of standing or sitting, especially in occupations requiring long hours on feet
- Sedentary lifestyle with a lack of regular exercise
- Smoking, which can affect blood circulation and vein health
Genetic and Biological Factors:
- Family history of venous disorders (hereditary predisposition)
- Age-related weakening of vein walls and valves
- Gender: women are more prone to certain venous conditions
Hormonal Influences:
- Pregnancy, due to increased blood volume and pressure on pelvic veins
- Hormonal medications like birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy
Medical Procedures:
- Certain surgical procedures, especially those involving the legs
- Catheterization or other invasive vascular procedures
Chronic Health Conditions:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Diabetes, which can affect blood vessels
- Chronic heart or lung diseases that impact circulation
When to Consult Your Healthcare Provider?
While some symptoms may be routine and can be reported during regular check-ups, others require immediate medical attention. By familiarizing yourself with these signs, you can ensure timely intervention and prevent potential complications. Here are some guidelines to help you determine when to reach out to your healthcare provider:
Routine Symptoms to Report:
- Persistent leg pain or discomfort
- Ongoing swelling in your legs or ankles
- Gradual changes in the appearance of your legs, such as:
- Skin color changes
- Development of varicose veins
- Dry or itchy skin
- Feelings of heaviness or tiredness in the legs
- Leg cramps, especially at night
Urgent Signs – Seek Immediate Medical Attention:
- Sudden or severe increase in leg pain
- Rapid or significant swelling in one or both legs
- Abrupt changes in skin color, particularly redness or unusual paleness
- Development of open sores or ulcers on the legs
- Signs of infection: warmth, redness, or fever
- Difficulty walking due to leg pain or swelling
How are venous leg ulcers treated?
The treatment of venous leg ulcers focuses on improving circulation and reducing swelling in the legs. Compression therapy, using special stockings or bandages, is the cornerstone of treatment, effectively managing swelling and promoting healing. Your healthcare provider may employ a range of additional strategies, including diagnostic tests to pinpoint the underlying cause, leg elevation exercises to improve blood flow, and proper wound care techniques. In some cases, surgical interventions may be recommended. The treatment plan is typically multifaceted and tailored to each patient’s specific needs.
Successful management of venous leg ulcers often requires a combination of these approaches, along with lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise and weight management. Your healthcare team will work with you to develop a comprehensive treatment plan, which may evolve over time based on your progress.
Surgical Options for Treating Venous Leg Ulcers
Your healthcare provider might recommend one of the following surgical options based on the severity of your condition and the underlying vein issues:
Endovenous Ablation:
- Minimally invasive procedure to close off damaged veins
- Uses heat (laser or radiofrequency) to seal these problematic veins
- Redirects blood flow to healthier veins
Vein Ligation and Stripping:
- Traditional surgical method for removing or tying off damaged veins
- Ligation involves tying off veins to prevent blood flow
- Stripping removes the entire damaged vein
SEPS (Subfascial Endoscopic Perforator Surgery):
- Minimally invasive technique to address perforator vein incompetence
- Uses small incisions and a camera to locate and treat problematic veins
- Particularly useful for ulcers resistant to conservative treatment
Skin Grafting:
- Used for large or slow-healing ulcers
- Involves transplanting healthy skin to cover the ulcer site
- Promotes faster healing and reduces the risk of infection
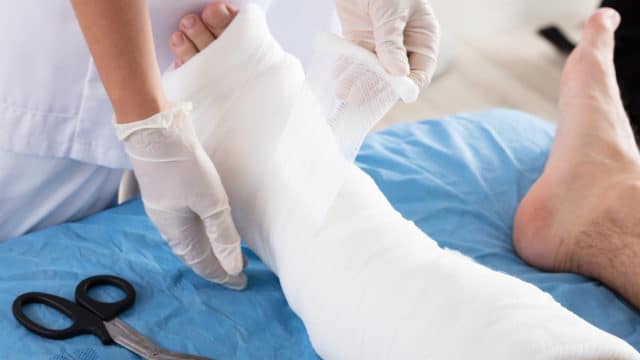
Compression is Key
Compression therapy is a cornerstone in the treatment of venous leg ulcers, utilizing specialized wraps, pumps, or stockings to improve circulation and reduce swelling. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions on how to use these compression garments effectively, as proper application is crucial for optimal results. During the active wound healing phase, you may need to wear compression garments continuously, even up to 24 hours a day.
Compression therapy doesn’t end when your wound heals; many patients need to continue wearing compression garments long-term to prevent recurrence and manage underlying venous insufficiency.
In addition to compression therapy, your treatment plan may include advanced wound care techniques to promote faster healing. Your healthcare team might use specialized dressings that create an optimal environment for wound healing, topical medications to prevent infection or stimulate tissue growth, and custom wraps to protect the wound while maintaining compression. Research has shown that in some cases, particularly for larger or stubborn ulcers, skin grafting may be beneficial. This can involve using your own skin (autografts) or bio-engineered tissue to cover the wound and accelerate healing. Your doctor will work closely with you to determine the most effective combination of treatments and therapies, tailoring the approach to your specific needs and monitoring your progress regularly.
Lifestyle Changes
By embracing key lifestyle changes, you can significantly accelerate your healing and reduce the risk of ulcer recurrence. Focus on maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, particularly walking, which helps improve circulation in your legs. If you smoke, quitting is one of the most impactful steps you can take for your overall vascular health. Remember, these changes not only support faster wound healing but also contribute to your long-term well-being.
Choosing the Right Treatment Approach
At Healogics, we’re committed to educating communities about treatment options for venous insufficiency. That’s why we’re here to help you take proactive steps in managing your vein health.
Choosing the right approach for venous insufficiency depends on various factors, including your individual health needs, lifestyle, and treatment goals. By working closely with your healthcare providers, you can develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific concerns and maximizes your chances of success.
Take the first step towards better vein health today—contact your nearest Healogics Wound Care Center®. We specialize in research-based care to heal your wound faster. Our team of experts can provide comprehensive care, from early wound intervention to advanced therapies for venous ulcers.
Click here to find a Healogics Wound Care Center® location near you and take control of your vein health today!
Source
Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurses Soceity. (2005). Guidelines for management of wounds in patients with lower-extemity venous disease. Glenview, IL. WOCN