Peripheral Artery Disease: Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options
At Healogics, we’re committed to raising awareness about peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition that affects nearly 10 million Americans. Despite its prevalence, PAD often goes undiagnosed, which is why we believe that understanding its symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is crucial for everyone’s health.
We often encounter confusion between PAD and venous insufficiency, another serious cardiovascular condition. While both can affect the lower extremity, they’re distinct in their causes and effects:
- PAD is an arterial disease affecting the vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
- Venous insufficiency involves the veins, which return blood to the heart.
Peripheral Artery Disease Awareness Month in September shines a spotlight on this cardiovascular condition. Many dismiss the mild to moderate leg pain associated with PAD as a normal part of increasing age. Raising awareness of PAD is crucial to encourage screenings for adults over 60 and promote lifestyle changes to help prevent PAD.
Understanding Peripheral Artery Disease: A Critical Step Toward Better Health
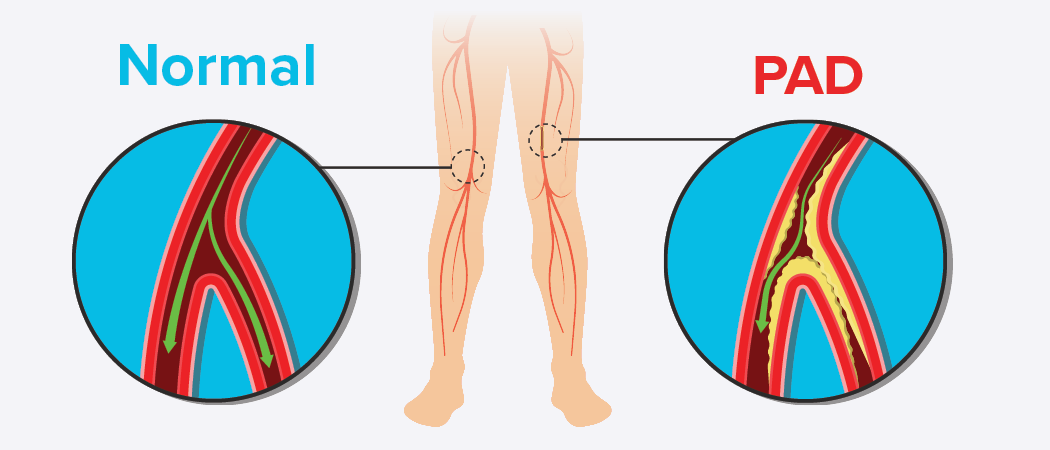
Peripheral artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to our limbs, most commonly the lower extremity of our legs, become narrowed or blocked. This reduced blood flow can lead to a range of symptoms and, if left untreated, may result in serious complications, including non-healing wounds and even amputation.
The symptoms of PAD can be subtle at first, which is why we emphasize the importance of early detection and treatment. The risks are high, too. PAD’s impact can extend beyond the limbs, significantly affecting overall health, including cardiovascular health. PAD belongs to a group of cardiovascular conditions that require vigilant monitoring and proactive management.
What causes PAD and who is at risk?
PAD occurs when plaque accumulates in the arteries that supply blood to areas beyond the heart. This plaque consists of fatty deposits influenced by many factors, including elevated cholesterol levels, heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and smoking. A family history of artery disease increases the risk. However, lifestyle choices, particularly diet and exercise, can play a significant role in maintaining arterial health.
What are the symptoms of PAD?
PAD Patients commonly experience leg pain during or after physical activity, as well as leg numbness. Numbness or tingling sensations in the feet and toes are also frequent indicators. Additional signs include cold or bluish skin and areas of shiny skin with noticeable hair loss. While these symptoms are concerning, the most critical sign of PAD is a foot ulcer or wound that shows no signs of healing after four weeks.
When left untreated, Peripheral Artery Disease symptoms tend to worsen over time, potentially leading to severe complications. Initial discomfort during physical activity may escalate to constant pain, even at rest. Numbness and tingling can lead to a loss of sensation, increasing the risk of unnoticed injuries. Skin changes may become more pronounced, with the affected areas becoming increasingly discolored and prone to ulcers.
In advanced stages, reduced blood flow can lead to critical limb ischemia, characterized by severe pain, non-healing wounds, and tissue death. This progression can, in extreme cases, require amputation. Additionally, advanced PAD can be a sign of widespread atherosclerosis, significantly increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
How is PAD diagnosed?
Your doctor may suspect PAD just by taking your pulse or examining a non-healing wound. To diagnose PAD, Healogics primarily uses the latest technology: a simple and painless test called a Doppler ultrasound. This test evaluates blood flow in the arteries and helps identify circulation issues and potential blockages. When appropriate, an Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) test may be performed. The ABI test compares blood pressure in the ankle and arm, while the Doppler ultrasound assesses blood flow directly.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Artery Disease
Treatment for Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) typically begins with lifestyle modifications. These include quitting smoking, achieving a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and adopting a healthy diet. In addition to these changes, doctors may prescribe medications to improve blood flow, such as antiplatelet drugs or those that help dilate blood vessels.
For more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. These procedures directly address arterial blockages: angioplasty uses a balloon to widen narrowed arteries, often combined with stent placement to keep them open. Bypass surgery creates an alternative route for blood flow around severely blocked arteries. Each of these approaches, either individually or in combination, works to improve blood flow to affected areas, helping to heal PAD symptoms such as pain, numbness, and poor wound healing. Your healthcare provider will determine the best treatment plan based on the severity of your condition and overall health, often combining multiple approaches for optimal management of PAD.
Peripheral Artery Disease vs. Venous Insufficiency
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) and Venous Insufficiency are two distinct circulatory conditions that can affect the limbs. PAD occurs when arteries narrow due to atherosclerosis, reducing blood flow to the legs. It’s often associated with risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels. Symptoms typically include leg pain during activity, weak pulses, and wounds that are slow to heal.
Venous Insufficiency, on the other hand, results from weakened veins, often due to blood clots or varicose veins. Risk factors include obesity and prolonged standing. Symptoms include swelling, aching legs, and skin changes.
The key difference is that PAD affects arteries—blood flow to the legs, while Venous Insufficiency affects veins—blood flow from the legs. PAD pain usually occurs during activity, whereas Venous Insufficiency causes discomfort after long periods of inactivity.
Treatment for PAD focuses on improving blood flow through lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery. Treatment of Venous Insufficiency aims to help blood return to the heart, often using compression stockings and leg elevation. For both conditions, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are vital to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
How does PAD affect wound healing?
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) increases the risk for patients developing non-healing wounds on their legs and feet. This is due to reduced blood flow, which limits the supply of oxygen and nutrients essential for healing. PAD is a significant factor in 10-30% of all lower limb ulcers. For PAD patients with wounds, proper care is necessary. Effective wound care helps to promote healing, prevent infections, and reduce the risk of complications that might lead to hospitalization. If you have PAD and notice a slow-to-heal wound, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly for appropriate treatment and care.
Best Practices for Managing Peripheral Artery Disease
While there is no cure, living well with Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) starts with taking an active role in your health. Regular exercise, particularly walking, can significantly improve circulation and reduce symptoms. Aim for at least 30 minutes of activity most days, starting slowly and gradually increasing as tolerated. Make sure your diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats and sugars. Smoking increases the risk of complications—quitting is crucial; consult your doctor for cessation resources.
Manage related conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure as directed by your healthcare provider. Practice good foot care by inspecting your feet daily and wearing comfortable, well-fitting shoes. Attend regular check-ups and take prescribed medications consistently. Stay informed about your condition, and don’t hesitate to ask questions. Remember, you are the most important member of your healthcare team. By actively managing your PAD, you can improve symptoms, slow disease progression, and enhance your overall quality of life. If you notice any changes in your condition, promptly seek medical advice.
Wound Care for Peripheral Artery Disease
Wound care belongs at the forefront of managing Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD), especially when ulcers or sores develop on the lower extremities. PAD patients are prone to non-healing wounds due to reduced blood flow, which limits oxygen and nutrient supply to injured tissues. Proper wound care is essential to promote healing, prevent infections, and reduce the risk of complications that could lead to hospitalization or amputation. Specialized wound care centers play a vital role in treating these complications. With extensive experience and expertise, wound care centers provide treatments tailored to each patient’s unique needs, helping to restore health, mobility, and quality of life.
Early detection and comprehensive treatment are the best tools for managing PAD effectively. It’s essential to understand the symptoms, such as leg pain during activity and slow-healing wounds, and recognize the risk factors like smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol. Treatment options range from lifestyle modifications to medications and, in severe cases, surgical interventions.
Please seek professional medical advice if you suspect that you might have PAD or notice any concerning symptoms. With proper management and care, including specialized wound treatment, when necessary, individuals with PAD can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of serious complications.
Healogics helps patients with chronic wounds heal faster. With over two decades of experience, we’ve successfully treated more than four million wounds. Our commitment to excellence extends beyond our Wound Care Centers; we actively partner with leading academic and research scientists to drive innovation in wound care.
With over 600 Wound Care Centers® nationwide, our team of specialists is ready to provide expert care when you need it most. Remember, you don’t need a referral to seek our help – we’re just a click or call away.